
Managing Diabetes Through








The recipes compiled here are meant to help you create an eating plan that works for you. There is variety to choose from and fit your needs. There is no need for deprivation; it is mostly exchanging poor food choices for healthier food choices! Whole grains, fresh fruits and vegetables, lean meats, and beans make wonderful and healthy diabetic meals. Fresh herbs are also a brilliant addition to any dish – especially when you need low-fat or low-sodium meals! Snacks and desserts can also be enjoyed; with adjustments to the recipe, and in moderation, many favorites can be diabetic friendly and still taste amazing!
Recipes for diabetics do not have to be bland, can be suited for vegetarians and vegans, and can include dessert. The recipes you will find here are also fantastic for when you are entertaining guests, have a special occasion, or when life calls for a special indulgence. We all need comfort food now and then – right?!
I believe that home-cooking tastes better, is healthier, and it does not have to be difficult – it can also save you money which is very nice! In this e-book you will find a variety of recipes that will keep your menus lively and flavorful.
There are several types of diabetes, levels of severity, and stages. Additionally, each person is different which is why it is vital to consult your healthcare practitioner before embarking on the journey to control your diabetes.

Food choices and exercise are critical to the success of managing diabetes and these are changes you can personally make. I have heard the phrase “too much sugar is bad for you” since I was a kid. I found out there is profound truth in this phrase after researching what high blood glucose does to your body; as you will see further down, high blood glucose causes great failures in a diabetic’s body.

Since carbohydrates play a significant role in a diabetic nutritional plan, look through the recipes and choose one that fits into your daily plan. When you plan out an eating program, you will find it is easier to create a balance that meets your nutritional needs and goals. Stocking up on the ingredients is another way to make your life a lot easier!

Exercise not only makes you feel better mentally, it makes your body feel good as it promotes better functioning of your body’s systems. Diabetics need this boost to help avoid, or repair, damage due to diabetes.




Remember, talk with your healthcare practitioner prior to beginning any exercise regimen to determine whether you should avoid certain forms of exercise.
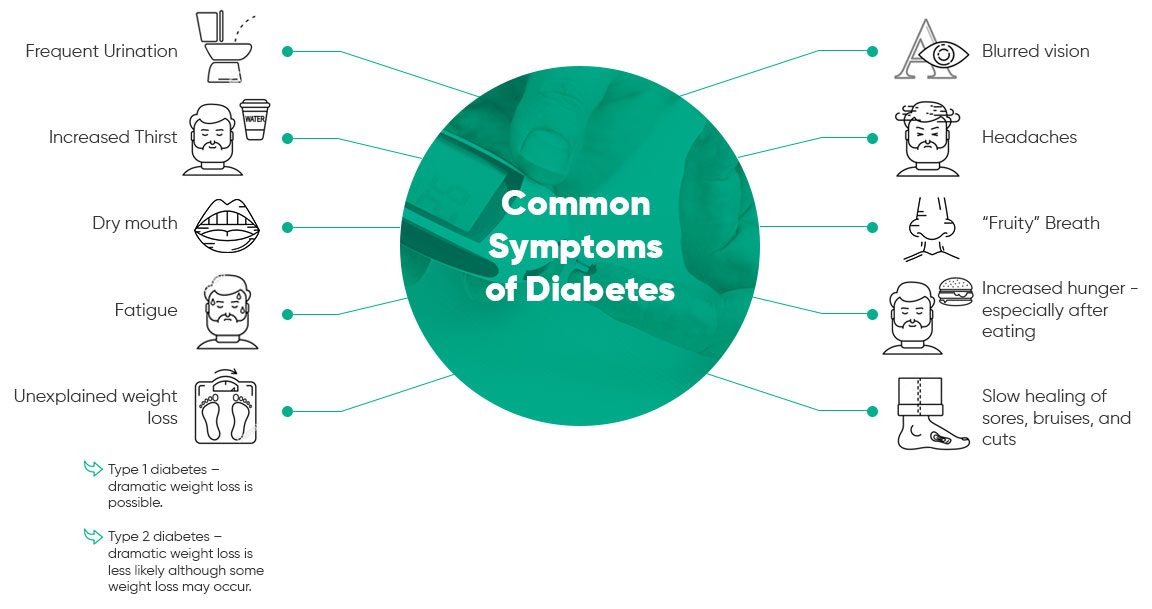
To make effective changes in your diet and lifestyle, it is important to have a base knowledge of diabetes. Equally essential to having the tools to create your diet and lifestyle plan is understanding what changes to make and why these changes are important. Please understand that the following lists are not comprehensive but intended to give an overview – or basic understanding – of symptoms to look for, what diabetes does to your body, potential complications, and what you can do to keep your body healthy.
 Potential causes of insulin resistance:
Potential causes of insulin resistance:
Poorly controlled diabetes may damage your body. While some conditions are less severe than others, it is important to be aware and be in tune with what is happening to your body.
Controlling your blood glucose is imperative to proper functioning of your body; too high blood glucose causes extreme problems for diabetics.
Ketoacidosis:
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS):
Hypoglycemia (low blood glucose):
Diabetic Nephropathy:
High blood glucose causes kidney damage and may lead to kidney failure.
Diabetic Retinopathy:
Diabetic Neuropathy:
 Gangrene is dangerous and can result in amputation.
Gangrene is dangerous and can result in amputation.Atherosclerotic Heart Disease (also known as Coronary Artery Disease and Ischemic Heart Disease):
Blockage of blood vessels to the heart causing a heart attack.
Arteriosclerotic Cerebrovascular Disease:
Arteriosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease:
Blood vessels in the legs can become blocked and result in the need for amputation of the legs or feet.
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD):
Eyes:
Mental health:
Hearing:
Loss of hearing due to high blood glucose damaging the auditory nerves.
Gastroparesis:
Muscles in the stomach stop functioning properly due to nerve damage caused by high blood glucose.


